Capillary Water In Soil Causes

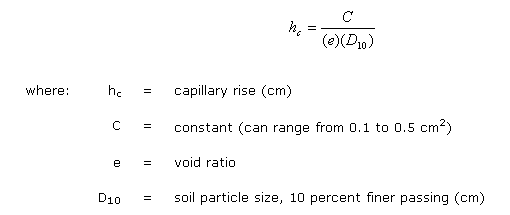
6 8 0 15 d10 mm hc m as you would expect finer the soil smaller the capillary tube diameter and.
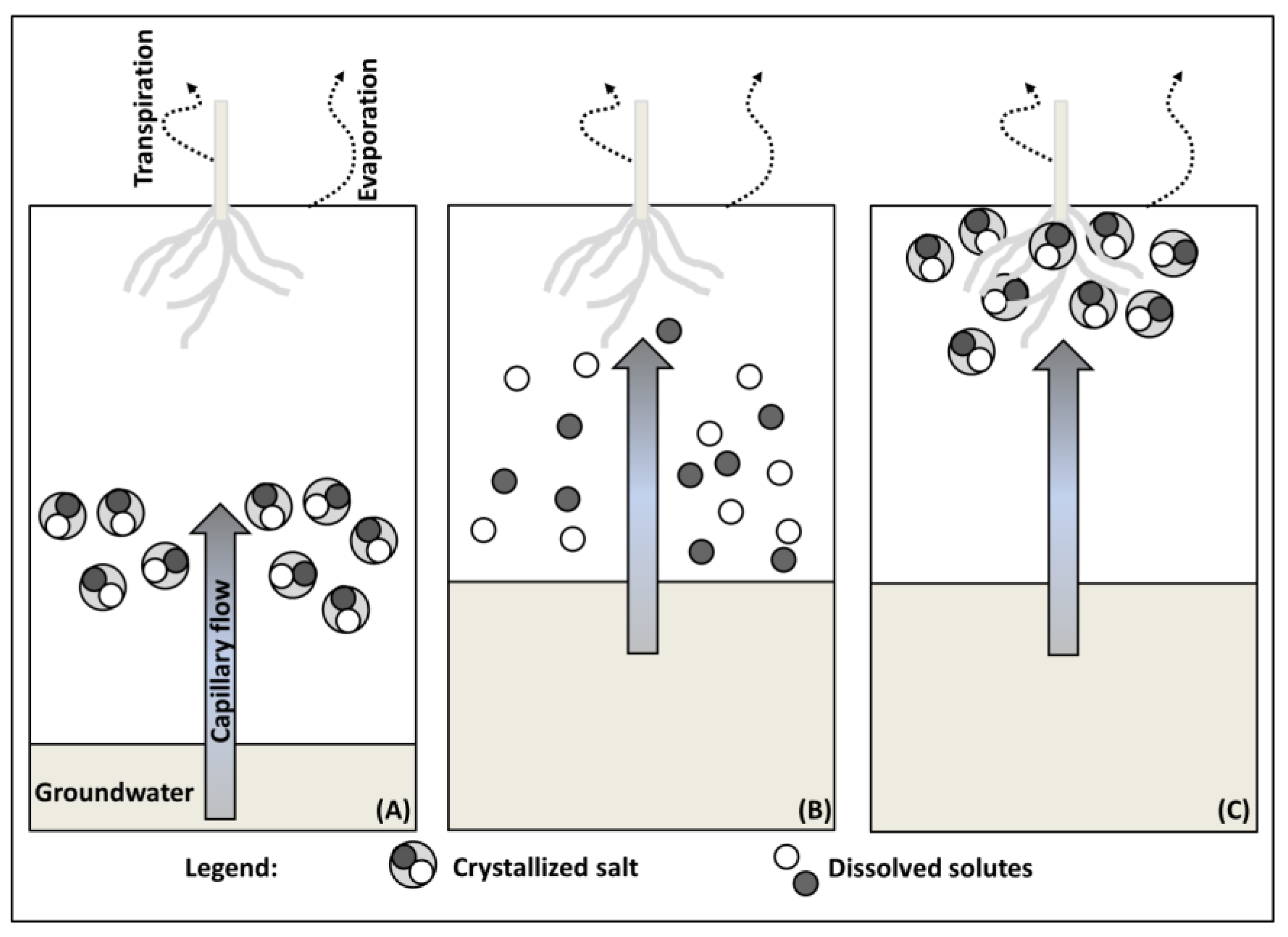
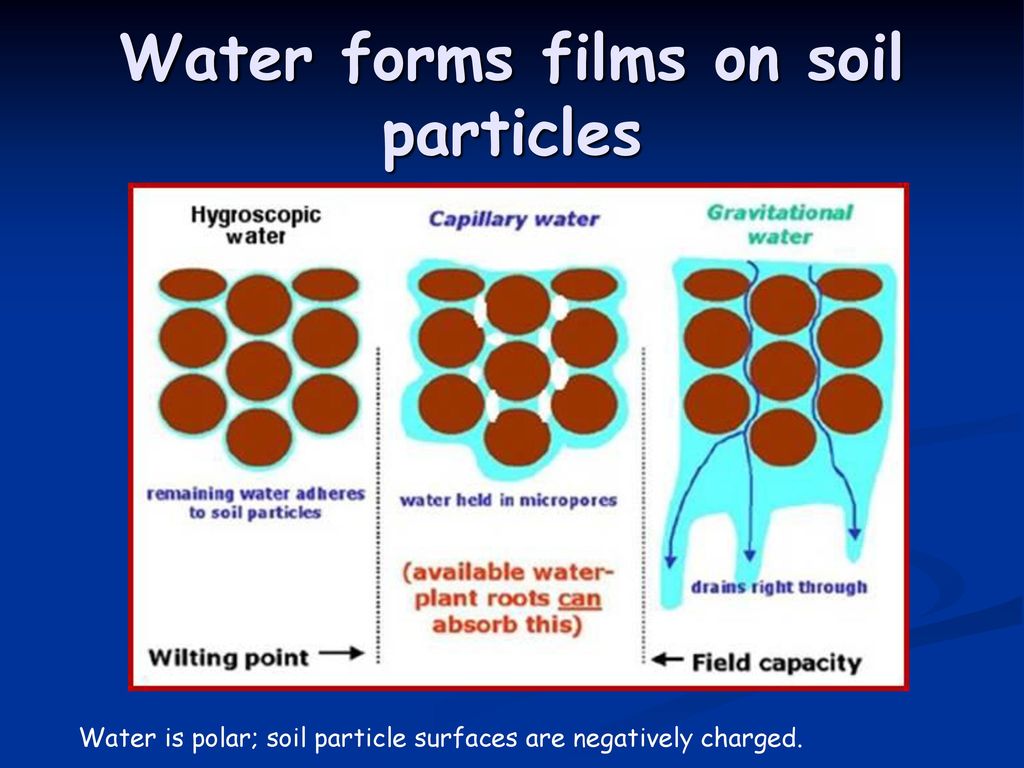
Capillary water in soil causes. It is primarily this capillary water which is readily available to the plant and this is the source of practically all the water a plant extracts from the soil. The best technique to keep capillary hang water in the soil is to add a layer of loose surface soil. And so the water evaporates. The height the capillary rise is inverse.
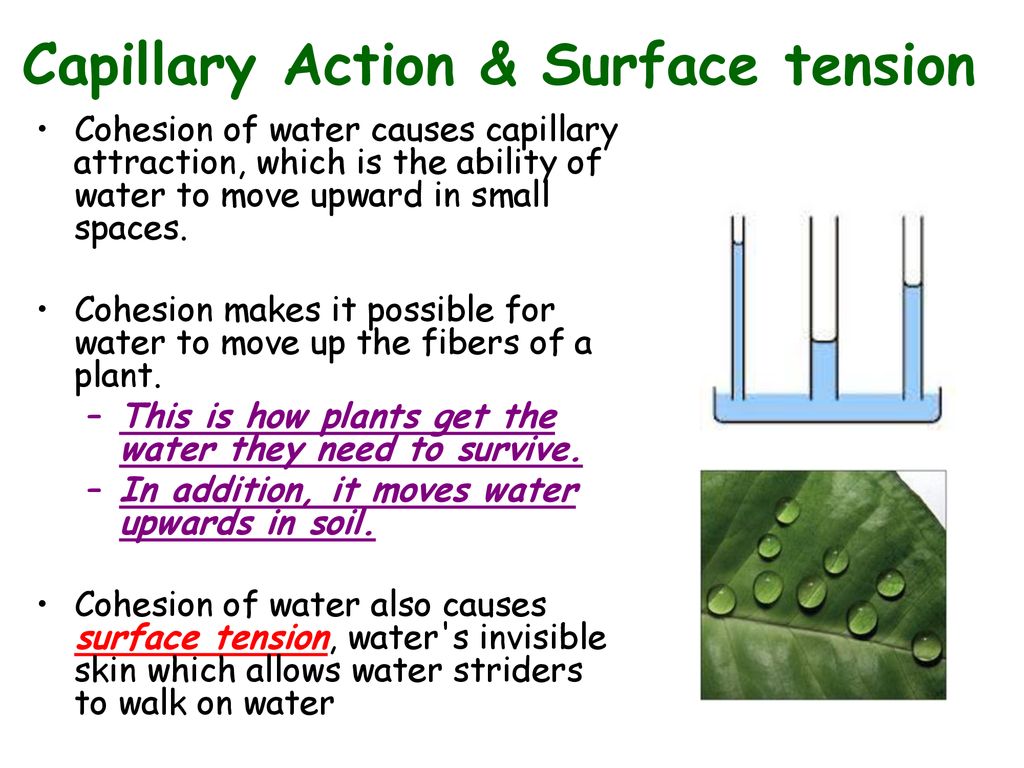
Capillary water is held in the soil because the surface tension properties cohesion and adhesion of the soil micropores are stronger than the force of gravity. Consequently a common apparatus used to demonstrate the phenomenon is the capillary tube when the lower end of a glass tube is placed in a liquid such as water a concave meniscus forms. Plants put down roots into the soil which are capable of carrying water from the soil up into the plant. In the occurrence of ground water in the u s.
Adhesion occurs between the fluid and the solid inner wall. During the day capillary water evaporates because of the sun s heat hitting the soil. Capillary action helps bring water up into the roots. The soil still contains some water but it is too difficult for the roots to suck it from the soil see fig.
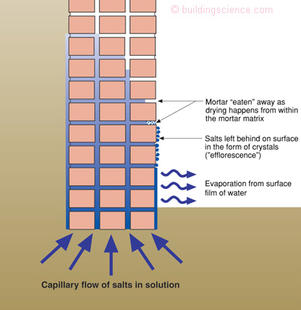
Owing to evaporation from the soil surface and absorption by roots the capillary water held by the soil is gradually depleted. This is capil lary water. Capillary penetration in porous media shares its dynamic mechanism with flow in hollow tubes as both processes are resisted by viscous forces. 2 4 available water content.
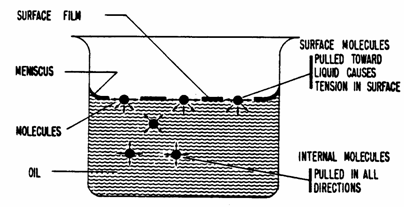
The water in a capillary tube is held up not only by the attraction of the walls of the tube for the water but by this attraction acting through the cohesion of the water. With a discussion of principles usgs water supply paper 489 1923 oscar e. Cohesion causes water molecules to stick to one another and form water droplets. The soil water content at the stage where the plant dies is called permanent wilting point.
Water will rise in the tube and form a meniscus as shown in the diagram. Plants and trees couldn t thrive without capillary action. Water which contains dissolved nutrients gets inside the roots and starts climbing up the plant tissue. However as the soil dries out the pore size increases and gravity starts to turn capillary water into gravitational water and it moves down.
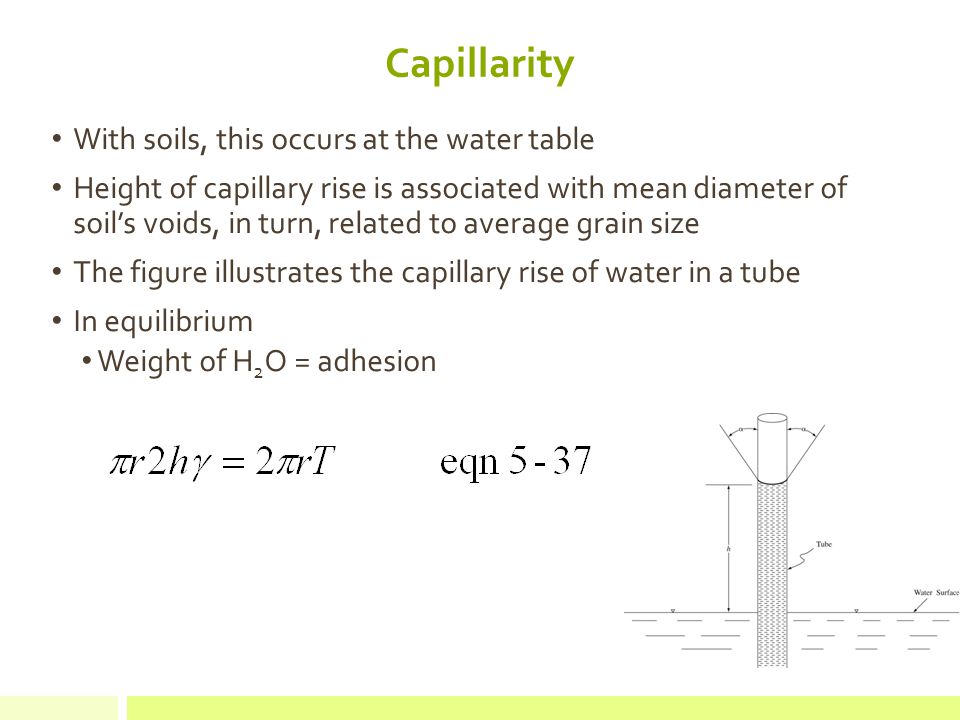
Therefore the capillary rise within a soil can be written as. Some soil moisture characteristics. The soil can be compared to a water reservoir for the plants. Meinzer states the reason for this attraction of the water for the walls of the tube as follows.
The capillary tube diamater of a soil is approximately 1 5 of d10. To help understand capillary water in soil it is helpful to review capillary action in a small glass tube inserted into water. Capillary tubes not straight though and allow the water to rise well above the water table.


.PNG)